Justin's Project Portfolio Page
Project: OutBook
OutBook is a desktop application designed for freelance insurance agents, enabling them to effectively organize and oversee their extensive contacts and meeting schedules. Users can link their contacts to their meetings, to keep track of the people attending these meetings.
My contributions to the project are listed below.
-
Code contributed: RepoSense link
-
New Features:
- Added
LastContactedTimefield to Person (Pull Request #90)- What it does: Allows a user to add a Person’s last contacted time when creating or editing a contact. This allows the user to keep track of uncontacted clients.
- Justification: This allows for the completion of meetings to automatically update a Person’s LastContactedTime field to the time of the meeting.
- Highlights: Implementation of this feature required extensive modification to the Model and Storage components, with many predicate classes having to be added to increase coupling and reduce cohesion within the app.
- Implemented Delete Meetings Command:
deletem(Pull Request #58)- Justification: There may be various reasons for a user to delete a meeting, such as cancellation.
- Added
-
Project management:
- Forking workflow
- Contributed issues
- Review and merge pull requests
- Reviewing documentation
- Forking workflow
-
Enhancements to existing features:
- Added utility method
TitleContainsKeywordsPredicate. (Pull Request #58)- What it does: Enables filtering of meetings by matching keywords to the meetings’ title.
- Justification: Lays the groundwork for the
findmfind meeting command, where users can use fields such as title, time, location, tags or attendees to search for a specific meeting.
- Configured storage to use a different file to store user data. (Pull Request #156)
- Added utility method
-
Documentation:
- User Guide
- Added documentation for
deletem. - Updated documentation for the following features:
addc,editcandaddm. - Modifed large parts of documentation to ensure coherence and consistency with codebase.
- Added documentation for
- Developer Guide
- Added implementation notes and diagram for
LastContactedTimefield - Non-functional Requirements
- Glossary
- Added implementation notes and diagram for
- User Guide
Contributions to the Developer Guide (Extracts):
- Added documentation for implementation of
LastContactedTimeobject:
Keeping track of last meeting with contact
Keeping track of the user’s last meeting with their contact is facilitated by the addition of a LastContactedTime object to Person.
Thus, each instance of Person will contain an immutable LastContactedTime object that stores the user’s last meeting with that contact.
The following steps shows how LastContactedTime is implemented and utilized in the application.
Step 1. The user inputs the addc command into the CommandBox input field, with the added field l/[LAST_CONTACTED_TIME].
The following diagram summarizes steps 2 to 6:
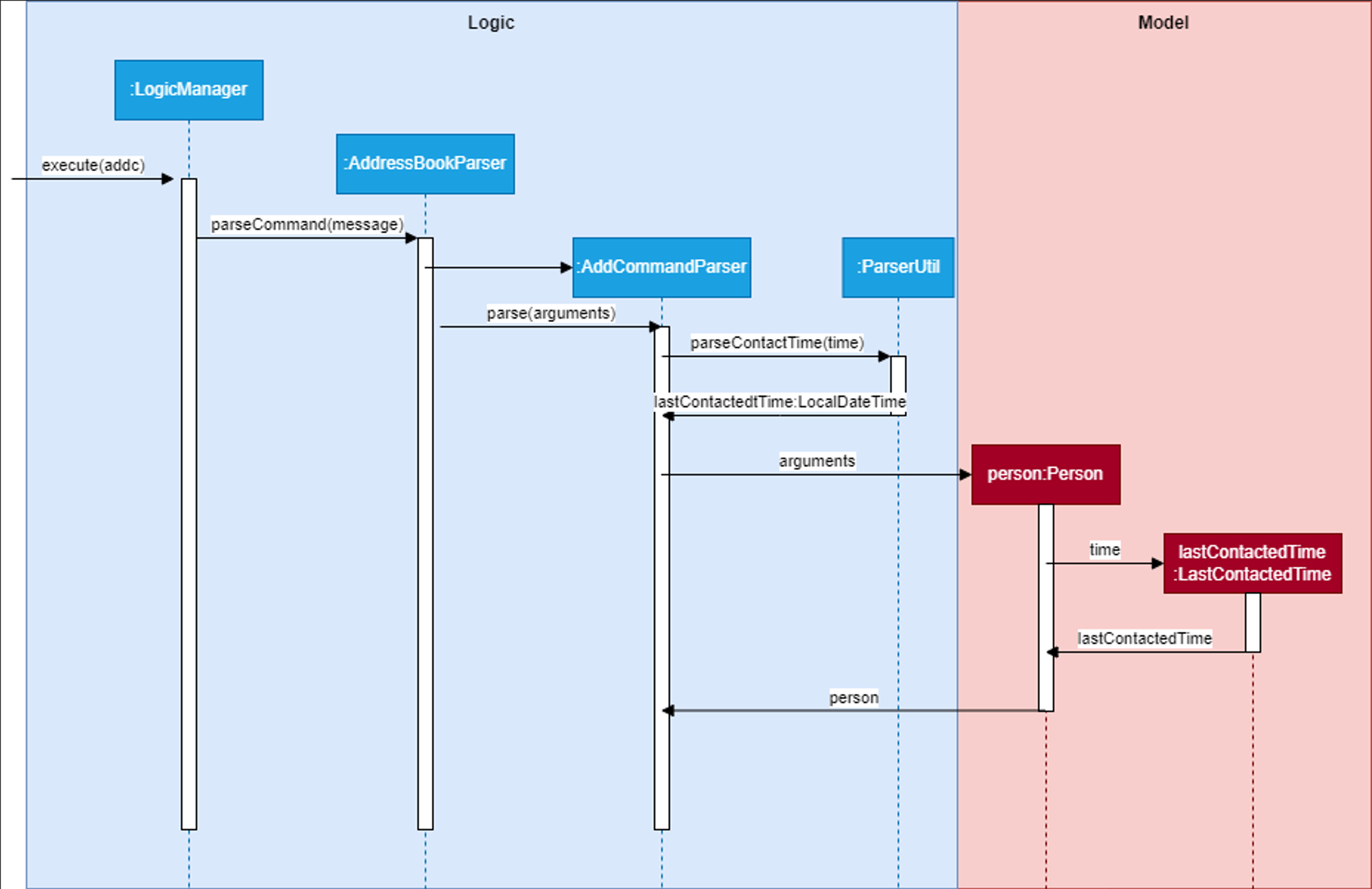
Step 2. Entering a correct command with the Enter key then calls execute on LogicManager.
Step 3. LogicManager then calls AddressBookParser#parseCommand(commandText) on the commandText String, which recognizes that it is an addc command.
Step 4. AddressBookParser then calls AddCommandParser#parse() on the command arguments.
Step 5. AddCommandParser then calls ParserUtil#parseContactTime() which parses the last contacted time and returns a LocalDateTime object called lastContactedTime.
Step 6. The lastContactedTime object is then passed to the Person constructor, which creates a new Person that calls the LastContactedTime constructor with it.
The following diagram summarizes steps 7 and 8:
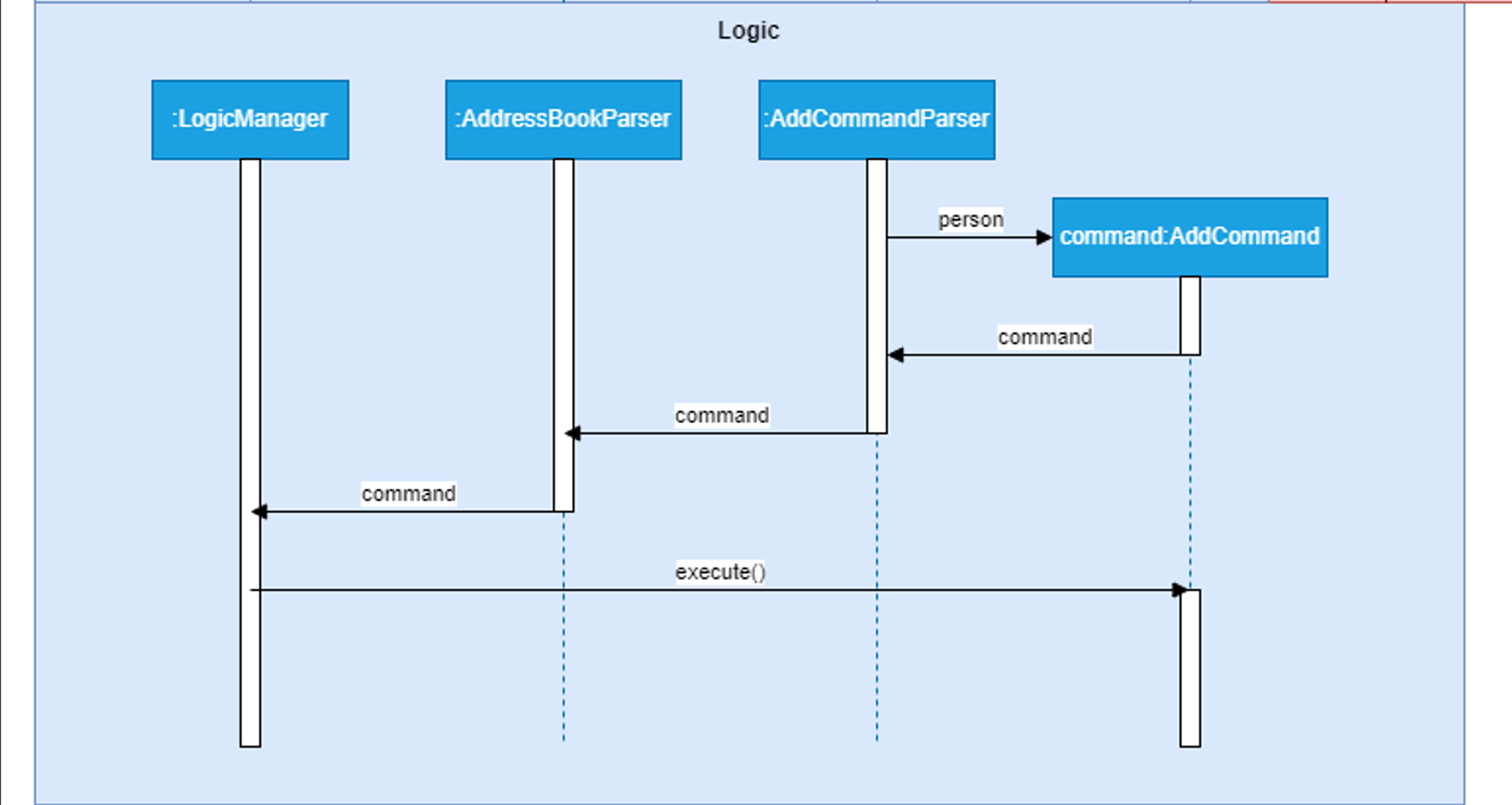
Step 7. The completed Person is passed to an AddCommand constructor which return a new AddCommand that can be executed.
Step 8. LogicManager then executes the AddCommand on the application model.
Step 9. Further execution is carried out, which like before adds the Person object to the list of Persons in the Model, and updates the Storage with this new Person.
Design Consideration: Updating last meeting with contact
Solution:
This is facilitated by the addition of the MarkDoneCommand. When a meeting is marked as done, the attendees of the meeting will be updated with their LastContactedTime field updated to the end time of the meeting.
- Added documentation for Non-Functional Requirements:
Non-Functional Requirements
Performance
- Should be able to respond to user input within 2 seconds under normal operating conditions.
- Should be able to handle a database of up to 1000 contacts and 500 meetings without a significant performance degradation.
Reliability
- Data integrity should be ensured under any usage conditions through automatic data backup.
Usability
- A user with above average typing speed for regular English text (i.e. not code, not system admin commands) should be able to accomplish most of the tasks faster using commands than using the mouse.
- Application GUI should be intuitive wherever possible, to reduce training for new users.
Documentation
- User documentation should include a comprehensive user manual.
- Developer documentation should cover the architecture, code structure, and guidelines for future development.
Compatibility
- Should work on any mainstream OS as long as it has Java
11or above installed.
- Added documentation for Glossary:
Glossary
- User Interface (UI): The point of interaction between a user and a software application, with both graphical and non-graphical elements.
- Application Programming Interface (API): A set of rules and tools allowing different software applications to communicate and exchange information.
- Command Line Interface (CLI): A text-based interface for interacting with a computer program or operating system, where users enter commands.
- Graphical User Interface (GUI): A visual interface using graphical elements like windows, icons, and buttons for user interaction with a software application.
- Mainstream OS: Windows, Linux, Unix, OS-X
- Private contact detail: A contact detail that is not meant to be shared with others
Contributions to the User Guide (Extracts):
- Added documentation for
deletem:
Deleting a meeting : deletem
Deletes a meeting from OutBook.
Format: deletem INDEX
- Deletes the meeting at the specified
INDEX. - The
INDEXrefers to the index number shown in the displayed meeting list. - The
INDEXmust be a positive integer such as 1, 2, 3, … - This command clears the meeting that is currently displayed via the
viewmcommand.
Examples:
-
listmfollowed bydeletem 2deletes the 2nd meeting in the results of thelistmcommand. -
findm m/Projectfollowed bydeletem 1deletes the 1st meeting in the results of thefindmcommand.
- Rewrote notes about command format for greater readability:
![]() Notes about the command format:
Notes about the command format:
-
Every word in uppercase represents a field you can supply.
e.g. inaddc n/NAME,NAMEis a parameter that can be substituted forJohn Doe, as inaddc n/John Doe. -
Fields contained in square brackets are optional.
e.g. when provided with the fieldsn/NAME [t/TAG], you can submitn/John Doe t/friendif you want to mark this contact as afriend, orn/John Doeotherwise. -
Fields with
… after them can be submitted any number of times, including zero.
e.g. when provided with the field[t/TAG]…, you can leave the field blank, or submitt/friend,t/friend t/family, etc. -
You can submit fields in any order.
e.g. if the command specifiesn/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER, submitting in the formatp/PHONE_NUMBER n/NAME, such as inp/91472381 n/John Doe, is also acceptable. -
If you are using a PDF version of this document, be careful when copying and pasting commands that span multiple lines. This is to avoid deletion of space characters surrounding line-breaks when lengthy text is copied over to the application.